22 February 2018
|
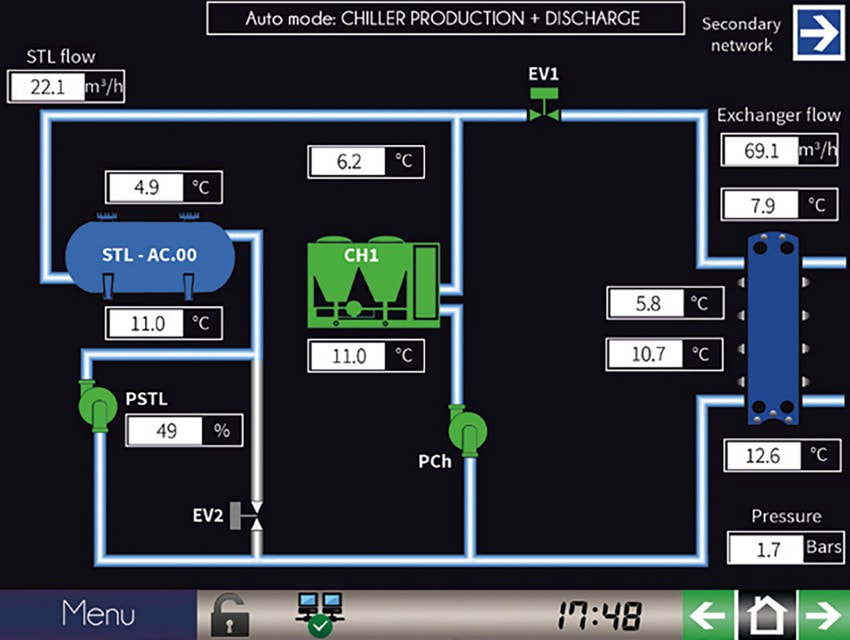
| CIAT Group and subsidiary Cristopia Energy Systems has launched a thermal energy storage system in the UK and says it helps to reduce the load on chiller and electrical power requirements by between 30 and 70 per cent for cooling production. The CIAT Cristopia system is designed to reduce end users’ energy costs by shifting away from reliance on peak day-time power by harnessing off-peak electricity at night. It reduces the load on the chiller by smoothing-out peaks in the daily load profile, in the process also reducing chiller maintenance costs and the size of the combined refrigerant charge on a site. |
Cristopia systems can be used for both air conditioning in buildings and industrial process applications. Air conditioning systems are traditionally designed to satisfy needs on the hottest days of the year, while industrial refrigeration systems often supply cooling energy for short high-consumption periods, corresponding to production cycles.
David Dunn, Managing Director of Toshiba Air Conditioning and CIAT in the UK, said: “In the age of ever-rising refrigerant costs, and increasingly stringent legal requirements around F-Gas, we believe opportunities to reduce refrigerant charge will be highly attractive to end users with significant cooling loads. With better regulated cooling production and delivery across the daily cycle, there is the added bonus of reduced noise as a result of smoothing out peak chiller operation.”
The system’s development is the result of 30 years’ collaborative research between Cristopia, technical centres and universities in France and across Europe. Applications include air conditioning systems for many types of commercial and public buildings, including shopping centres, hospitals, hotels, schools, airports, and leisure centres, plus industrial cooling for food manufacture, bottling and brewing plants, power generation, ice rinks and data centres.
The Cristopia solution also includes a monitoring and control system that optimises the performance and energy efficiency of the full installation, enabling end users to minimise energy use, and reduce carbon dioxide emissions and operating costs.
The system, also be available from Toshiba Air Conditioning in the UK, is used in more than 3000 installations around the world, transferring a combined 6 million kWh of electricity from peak to off-peak periods, saving more than 500MW of electricity.
David Dunn, Managing Director of Toshiba Air Conditioning and CIAT in the UK, said: “In the age of ever-rising refrigerant costs, and increasingly stringent legal requirements around F-Gas, we believe opportunities to reduce refrigerant charge will be highly attractive to end users with significant cooling loads. With better regulated cooling production and delivery across the daily cycle, there is the added bonus of reduced noise as a result of smoothing out peak chiller operation.”
The system’s development is the result of 30 years’ collaborative research between Cristopia, technical centres and universities in France and across Europe. Applications include air conditioning systems for many types of commercial and public buildings, including shopping centres, hospitals, hotels, schools, airports, and leisure centres, plus industrial cooling for food manufacture, bottling and brewing plants, power generation, ice rinks and data centres.
The Cristopia solution also includes a monitoring and control system that optimises the performance and energy efficiency of the full installation, enabling end users to minimise energy use, and reduce carbon dioxide emissions and operating costs.
The system, also be available from Toshiba Air Conditioning in the UK, is used in more than 3000 installations around the world, transferring a combined 6 million kWh of electricity from peak to off-peak periods, saving more than 500MW of electricity.
Content continues after advertisements